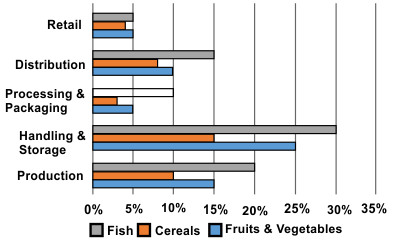
Q.3 |
Consider the case study given below and answer the following question:
Case Study: Protecting the Coral Reefs of Raja Ampat, Indonesia
Location: Raja Ampat, a stunning archipelago in Indonesia famed for its thriving coral reefs, biodiversity, and diving tourism.
Challenges:
-Overfishing: Unsustainable fishing practices, including blast fishing and cyanide fishing, have depleted fish stocks and damaged coral reefs.
-Pollution: Plastic pollution, agricultural runoff, and sedimentation from coastal development all threaten the delicate marine ecosystem.
-Climate Change: Rising ocean temperatures and acidification are bleaching and killing coral, the foundation of the reef ecosystem.
Initiatives:
-Marine Protected Areas (MPAs): Establishing and enforcing MPAs restricts harmful fishing practices and allows reefs to recover. Raja Ampat boasts one of the largest MPAs in Southeast Asia, covering over 1.5 million hectares.
-Community-Based Management: Local communities play a crucial role in protecting their reefs. The Coral Triangle Initiative focuses on empowering them through sustainable fishing practices and alternative livelihoods like ecotourism.
-Sustainable Aquaculture: Farming fish responsibly reduces pressure on wild stocks and provides alternative income for fishermen. Locally managed fish farms in Raja Ampat demonstrate successful alternatives to overfishing.
-Coral Restoration: Innovative techniques like coral nurseries and transplantation help regenerate damaged reefs and restore marine biodiversity.
Outcomes:
-Fish stocks are rebounding: The Raja Ampat MPA has shown a significant increase in fish biomass within its boundaries, demonstrating the effectiveness of protected areas.
-Improved water quality: Reduced pollution and sedimentation contribute to healthier corals and a more vibrant marine environment.
-Empowered communities: Local involvement in conservation fosters environmental stewardship and provides sustainable economic opportunities.
Raja Ampat serves as a beacon of hope in marine conservation, demonstrating the effectiveness of community-driven, multi-pronged approaches to protecting life below water. By tackling overfishing, pollution, and climate change, we can safeguard the future of these vital ecosystems and the communities that depend on them
What is a long-term challenge that the case study implies requires continuous global support to ensure the success of marine conservation in Raja Ampat?
|