1. Charles wants to conduct an experiment to study oscillatory motion. Which of the following setups would be suitable?
a) Observing the motion of a ball rolling down a slope
b) Measuring the distance covered by a bicycle on a straight road
c) Investigating the swinging motion of a pendulum
d) Analysing the rotational motion of a spinning top
Answer: c) A pendulum exhibits oscillatory motion as it swings back and forth. By observing and analysing the swinging motion of a pendulum the characteristics of oscillatory motion can be studied.
2. Which of the following is an example of non-uniform circular motion?
a) A spinning top slowing down gradually
b) A planet orbiting around the Sun
c) A car moving on a circular track at a constant speed
d) A pendulum swinging back and forth
Answer: a) Non-uniform circular motion refers to a motion where the speed of the object changes over time. In the case of a spinning top, as it slows down gradually, its speed decreases, indicating a non-uniform circular motion.
3. Objects can exhibit multiple types of motion simultaneously. Which of the following examples illustrates this phenomenon?
a) A car moving in a straight line at a constant speed
b) Clothes spinning in a washing machine
c) The hands of a clock ticking
d) A fan rotating
Answer: a) A car moving in a straight line at a constant speed exhibits both translatory motion (straight line movement) and rotational motion (the wheels rotating). Therefore, it is an example of an object exhibiting multiple types of motion simultaneously.
4. A stretched rubber band is plucked and left to quiver. What type of motion is observed?
a) Revolutionary motion
b) Translatory motion
c) Curvilinear motion
d) Vibratory motion
Answer: d) When a stretched rubber band is plucked and left to quiver, it undergoes back-and-forth motion. This motion is known as vibratory motion, characterised by oscillations or vibrations.
5. Match the following types of motion with their corresponding examples.
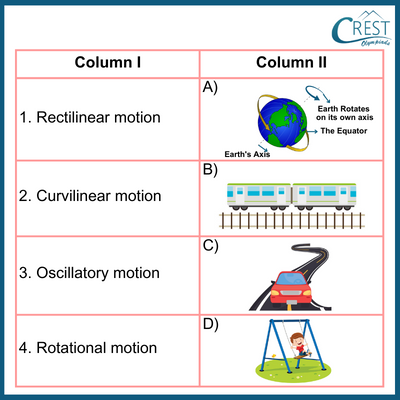
a) 1:C, 2:B, 3:D, 4:A
b) 1:B, 2:C, 3:D, 4:A
c) 1:A, 2:C, 3:B, 4:D
d) 1:C, 2:D, 3:B, 4:A
Answer: b) Rectilinear motion: Earth rotating on its axis
Curvilinear motion: Train moving on a straight railway track
Oscillatory motion: Car moving on a curved path
Rotational motion: Child on a swing moving back and forth


