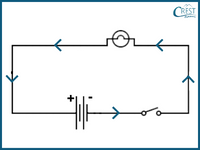
1. Consider the circuit diagram below. Based on the diagram, determine the state of the bulb in the circuit.
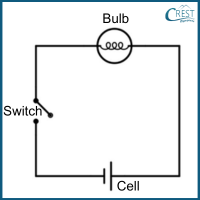
a) The bulb will glow.
b) The bulb will not glow.
c) The brightness of the bulb will be dim.
d) The brightness of the bulb will be bright.
Answer: b) The bulb will not glow.
In the given circuit diagram, the circuit is open, which means there is a gap or break in the path of the current flow. Without a complete circuit, the current cannot flow through the bulb, causing it to not glow.
2. Which of the following images correctly represents the direction of current flow in a closed circuit?
a)
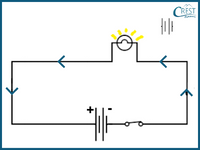
b)
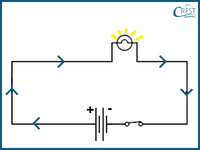
c)
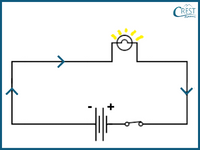
d)
Answer: b) In a closed circuit, the electric current flows from the positive terminal of the battery (represented by a longer line) or power source towards the negative terminal (represented by a shorter line). This flow of current occurs in a continuous loop, allowing electrical energy to be transferred and power the components connected in the circuit. Image B shows the direction of current flow from the positive terminal to the negative terminal, which aligns with the standard convention for current flow in a closed circuit.
3. Rachel connects a bulb and a battery using a long and thin copper wire. If he replaces the copper wire with a thicker aluminium wire, what is likely to happen to the brightness of the bulb?
a) The bulb will become brighter.
b) The bulb will become dimmer.
c) The brightness of the bulb will remain the same.
d) The bulb will stop glowing.
Answer: a) If Rachel replaces the thin copper wire with a thicker aluminium wire, the bulb is likely to become brighter. Using a thicker wire allows more current to reach the bulb. When more current flows through the bulb, it gets more energy, causing it to glow brighter.
4. Complete the following pattern:
Aluminium foil: Conductor:: ? : Insulator
a) Graphite pencil
b) Coin
c) Glass rod
d) Silver ring
Answer: c) The pattern suggests that aluminium foil is a conductor, and we need to find the insulator counterpart. Among the options, a glass rod is an insulator, as it does not conduct electricity.
5. A group of students conducted an experiment to determine whether certain materials were conductors or insulators. They connected a bulb and a battery using different wires made of different materials. Based on their observations, they recorded the following:
Wire A: Bulb glows brightly
Wire B: Bulb glows dimly
Wire C: Bulb does not glow
Which of the following conclusions can be drawn from the experiment?
a) Wire A and Wire B are insulators, but Wire C is a conductor.
b) Wire A is an insulator, Wire B is a conductor, and Wire C is an insulator.
c) Wire A is a good conductor, Wire B is a weak conductor, and Wire C is an insulator.
d) Wire A is a weak conductor, Wire B is a good conductor, and Wire C is an insulator.
Answer: c) From the observations, we can conclude that Wire A allows the current to flow freely, resulting in a bright glow of the bulb. This suggests that Wire A is a good conductor of electricity. Wire B, on the other hand, allows some current to flow, but the glow of the bulb is dim. This indicates that Wire B is a weak conductor. Wire C does not allow any current to flow, resulting in no glow of the bulb. Therefore, Wire C is an insulator, as it does not conduct electricity.






