1. A scientist is studying an organism (shown in the picture) with the following characteristics: unicellular structure, eukaryotic cells, autotrophic nutrition, chloroplast and the presence of flagella for movement. Identify the organism and the kingdom it most likely belongs to.

a) Cyanobacteria: Monera
b) Euglena: Protista
c)Lichen: Fungi
d) Sea Lettice: Plantae
Answer: b) The organism in the picture with the given characteristics (unicellular structure, eukaryotic cells, autotrophic nutrition, chloroplast, and the presence of flagella for movement) is most likely Euglena which belongs to the kingdom Protista.
2. Classify the following plants into Gymnosperms and Angiosperms:
I. Pine tree
II. Maple tree
III. Cycad
IV. Sunflower
V. Spruce tree
a) Gymnosperms: I, III; Angiosperms: II, IV, V
b) Gymnosperms: II, V; Angiosperms: I, III, IV
c) Gymnosperms: I, III, V; Angiosperms: II, IV
d) Gymnosperms: III; Angiosperms: I, II, IV, V
Answer: c) Gymnosperms: I, III, V; Angiosperms: II, IV
Gymnosperms: Pine tree, Cycad, Spruce tree
Angiosperms: II, IV: Maple tree, Sunflower
3. An expedition to a remote rainforest uncovers a new species of orchid with distinct floral characteristics. The scientists on the expedition are excited to document their discovery, including giving the orchid a scientific name. How does binomial nomenclature help them accurately classify and communicate about the orchid's features?
a) It allows them to choose a name based on the orchid's location in the rainforest.
b) It provides a standardised system for naming the orchid, ensuring clarity among scientists.
c) It enables them to assign a name that reflects the orchid's market value.
d) It eliminates the need to use scientific names in research publications.
Answer: b) Binomial nomenclature provides a systematic and consistent approach to naming organisms. By assigning a unique scientific name using the binomial format (genus species), scientists ensure that there is a standardised way to refer to the newly discovered orchid. This helps prevent confusion caused by common names that may vary between languages or regions.
4. On a field trip, students collected samples of various organisms from a pond ecosystem. They found algae, mosses, and ferns among the collected samples. What is the classification of these organisms based on your knowledge of plant diversity?
a) All are angiosperms
b) All are gymnosperms
c) Algae are pteridophytes, mosses are angiosperms, and ferns are bryophytes
d) Algae are thallophytes, mosses are pteridophytes, and ferns are pteridophytes
Answer: d) Algae are thallophytes, mosses are pteridophytes, and ferns are pteridophytes
5. Complete the following flowchart by accurately identifying A, B, C and D.
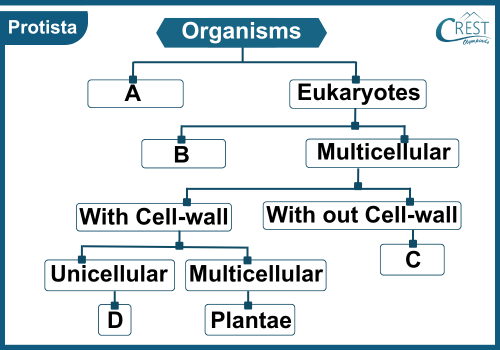
a) A: Prokaryotes, B: Unicellular, C: Animalia, D: Fungi
b) A: Bacteria, B: Unicellular, C: Alage, D: Fungi
c) A: Prokaryotes, B: Bacteria, C: Fungi, D: Monera
d) A: Prokaryotes, B: Monera, C: Protista, D: Monera
Answer: a) A: Prokaryotes, B: Unicellular, C: Animalia, D: Fungi



